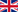
Publications in September 2011

In September a total of 62 articles were published in the field of chitosan. In this month the most publications came from China where 10 articles were published. With 7 articles India was in second place followed by the USA where 6 articles were published.
| Top Journals | Publications |
| J Biomater Sci Polym Ed | 5 |
| Tissue Eng Part A | 4 |
| Int J Pharm | 3 |
| J Colloid Interface Sci | 3 |
| J Biomed Mater Bes A | 3 |
Table: Journals with the most publications about chitosan and chitosan derivatives.
Below two articles about chitosan coatings are shortly introduced.
Chitosan-Based Ultrathin Films as Antifouling, Anticoagulant and Antibacterial Protective Coatings
M. Bulwan, K. Wójcik, S. Zapotoczny, M. Nowakowska, J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2011, 29.
Using layer by layer deposition methodology the team of Bulwan prepared ultrathin films from ionic derivatives of chitosan with antifouling, anticoagulant and antibacterial properties.
Silicon and glass surfaces protected by these nanocoatings were resistant to non-specific adsorption of proteins. Furthermore microscopic studies (SEM, AFM) and the MTT viability test showed that the formation of bacterial (Staphylococcus aureus) biofilms was prevented by the coatings.
The authors account these chitosan based protective coatings as promising for biomedical applications (for example as protective coatings for medical devices). In this case anticoagulant and antifouling properties are also important. These properties could be shown in the studies of Bulwan et al.
The studies also found the biologically relevant properties to be dependent on the thickness of those nanocoatings.
Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information
Development and characterization of chitosan coated poly-(ε-caprolacone) nanoparticulate system for effective immunization against influenza
N. K. Gupta, V. Sharma, V. K. Dixit, Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Dr. Hari Singh Gour University, Sagar, India (Vaccine. 2011 Sep 19.)
For an effective nasal immunization Gupta, Sharma and Dixit developed a carrier system in the form of a poly-(ε-caprolactone) nanoparticles coated with chitosan (CS-PCL). The characterization of the CS-PCL nanoparticles was effected in vitro for their percent yield, size, shape, entrapment efficiency, loading capacity and zeta potential. Also evaluated were the in vitro release and antigen integrity. As antigen they used recombinant Influenza A virus (A/California/07/2009) H1N1 hemagglutinin (HA) protein.
Determined values:
| size | 125.64 ± 6.51 nm (with narrow size distribution (PDI: 0.185 ± 0.032)) |
| positive surface charge | 22.88 mV |
| entrapment efficiency | 74.84 ± 4.51% |
| loading capacity and zeta potential | 14 ± 2% (w/w) |
| 66.47% of entrapped antigen was released within 63 days |
The positive results of a cogent immune response demonstrate high potential of the CS-PCL nanoparticle adjuvant for nasal administered influenza antigen carriers.
Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information
Source: GoPubMed
coating, antifouling, chitosan films, anticoagulant
- Created on .