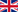
Publications in November 2011

So far November is the month with most publications in the year 2011. Overall 168 articles were published.
The three countries with the most publications are again:
China (53 Artikel),
India (20 Artikel) and the
USA (12 Artikel).
| Top Journals | Publications |
| International Journal of Biological Macromolecules | 13 |
| International Journal of Pharmaceutics | 10 |
| Journal of Material Science: Materials in Medicine | 10 |
| Biomacromolecules | 9 |
| Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces | 7 |
Table: Journals with the most publications about chitosan and chitosan derivatives.
Two articles about chitosan applications in the field of intestine research are being introduced below.
Coated chitosan pellets containing rutin intended for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: In vitro characteristics and in vivo evaluation
Rabišková M., Bautzová T., Gajdziok J., Dvořáčková K., Lamprecht A., Pellequer Y., Spilková J.; International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2011 Nov. 3. (Epub ahead of print)
The intention of the study was to prepare coated pellets which can be used for antioxidant rutin colon delivery. Furthermore the pellets had to be evaluated in vitro and in vivo (in experimental colitis in rats).
Overall three different coatings were prepared for this application:
- caffeic acid/hypromellose/alginic acid coating
- sodium alginate/hypromellose/zinc acetate coating
- sodium alginate/chitosan coating
In the research pellets with a sodium alginate/chitosan coating showed low rutin dissolution (12-14%) in upper gastrointestinal tract conditions. Under colon conditions a fast release (87-89%) was demonstrated.
After colitis induction and development in rats, pellets and a rutin solution were dispensed orally. Additionally there was a rectal application of the solution.
The orally dispensed sodium alginate/chitosan coated pellets and the rectally dispensed solution showed the best effects.
The combination of the natural product rutin, mucoadhesive chitosan that can be degraded in the colon and sodium alginate as main coating component in type of pellets is a promising preparation for the therapy of severe illness.
Quelle: US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health
Chitosan enhances transcellular permeability in human and rat intestine epithelium
Canali M. M., Pedrotti L. P., Balsinde J., Ibarra C., Correa S. G.; European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 2011 Nov. 20. (Epub ahead of print)
The transit of molecules from and into the organism is regulated by the intestinal epithelium. Different agents can enhance the absorption by inducing changes in both routes (transcellular and paracellular).
Chitosan can activate the intestinal epithelium cells and induce the release of regulatory factors which influence the immuno modulatory function of the epithelium cells.
The interaction between chitosan and the intestinal epithelium cells isn’t fully understood..
The mentioned research showed that chitosan enhances the transcellular permeability to ion, water and protein markers in human and rat colon samples. In contrast chitosan decreases the water permeability by the paracellular route.
The results are important for understanding the activity of chitosan in mucosal environment.
Source: US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health
Source: GoPubMed
- Created on .