Publications in November & December 2014

At the end of the year 2014 numerous articles about chitosan and chitosan derivatives were published. All in all 312 reports were released in November and December by leading scientists from China (89 articles), USA (35) India (28) and South Korea (21).
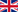
| Top Journals | Publications |
| Carbohydrate polymers | 22 |
| Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces | 12 |
| International journal of biological macromolecules | 10 |
| European journal of pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics | 8 |
| Journal of biomedical materials research. Part A | 7 |
| Materials science & engineering. C, Materials for biological applications | 7 |
Table: Journals publishing the highest number of chitosan-related articles in November and December 2014.
Source: GoPubMed
Almost one-third of these articles examined chitosan-modified nanoparticles. Two promising publications are presented below, displaying novel biotechnological approaches and application options of chitosan-modified nanoparticles.
Chitosan stabilized Prussian blue nanoparticles for photothermally enhanced gene delivery.
Li X.D., Liang X.L., Ma F. et al.; Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. Vol. 123:629-38; Nov. 2014
Gene therapy is a highly promising method, which proved to be clinical successful in the treatment of severe diseases. However, the efficiency of delivering nucleic acids (genes) to their site of action and the biosafety of carrier molecules (vectors) are often insufficient.
In this article a photocontollable gene delivery system was designed by modifying nanoparticles of Prussian blue with chitosan (CS/PB NPs). These positively charged nanoparticles are highly advantageous as they are:
- ultra-small size (∼ 3nm)
- physiological stable
- biocompatible, proven in in vitro and in vivo experiments
- photothermally enhanced gene transfection rate
- nonviral vector
CS/PB NPs display strong absorption efficiency of near infrared light (NIR). Upon NIR light stimulation these nanoparticles emit heat, which promotes their own uptake into the cells. In contrast to free polyethylenimine (PEI), a common transfection agent, CS/PB NPs possess superior transfection efficiency. Due to their physico-chemical properties, CS/PB nanovectors couldt be a promising tool to optimize the delivery and liberation of nucleic acids and to improve biosafety of gene therapy.
Source: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0927776514005323
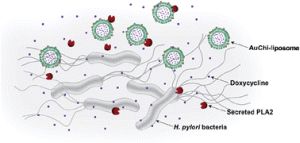
Phospholipase A2-responsive antibiotic delivery via nanoparticle-stabilized liposomes for the treatment of bacterial infection.
Thamphiwatana S., Gao W., Pornpattananangkul D. et al.; J Mater Chem B Mater Biol Med. Vol. 14;2(46):8201-8207; Dec. 2014
Liposomes are intensively studied, as they are capable to carry and deliver drugs in dependence of their environment. By adsorbing charged nanoparticles to the lipid surface, liposomes can be stabilized against fusion, while drug leakage is minimized.
The aim of this study was to develop a smart “on-demand” antibiotic delivery system. Chitosan-modified gold nanoparticles (AuChi) were adsorbed to the surface of liposomes. These AuChi liposomes display a significantly reduced payload leakage and no fusion activity.
The liposomes were composed of lipids, which could be degraded by the bacterial enzyme phospholipase A2 (PLA2). Pathological bacterial strains like Helicobacter pylori are capable to secrete PLA2 in order to modulate the inflammatory response of the host. AuChi-liposomes, applied to H. pylori cultures, display a rapid release of their encapsulated drugs. By loading liposomes with doxycycline, a tetracycline-based antibiotic used in the treatment of infectious diseases, the growth of H. pylori was successfully suppressed.
Conclusion:
 |
|
Source: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25544886?dopt=Abstract