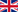
Publications in April 2015

In April 139 publications have been released about chitosan, which mainly focused on topics like evaluation studies, pharmaceutical preparations and nanoparticles. The leading nations in the field of chitosan research are China (48 articles), India (18) and USA (13).
| Top Journals | Publications |
| International journal of biological macromolecules | 24 |
| Materials science & engineering. C, Materials for biological applications | 8 |
| International journal of pharmaceutics | 6 |
| Macromolecular bioscience | 5 |
| ACS applied materials & interfaces | 5 |
Table: List of scientific journals, which published the highest number of chitosan-related articles in April 2015.
Source: GoPubMed
Chitosan and several chitosan derivatives are intensively studied for their drug delivery potential. Here we present two novel studies about chitosan-based nanoparticles, which might be interesting for different fields of research.
Fabrication and Characterization of Gd-DTPA-Loaded Chitosan–Poly(Acrylic Acid) Nanoparticles for Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Ahmed A., Zhang C., Guo J et al.; Macromolecular Bioscience. doi: 10.1002/mabi.201500034. [Epub ahead of print] April 2015
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical scanning technique, which visualizes soft tissue structures by using an oscillating magnetic field. The authors of the present study developed chitosan-poly (acrylic acid)-based nanoparticles (CS-PAA) and adsorbed gadolinium-diethylenetriaminepentacetate (Gd-DTPA) to the particle surface.
Gd-based contrast agents are commonly used for MRI tomography, as they can improve imaging signals. Gd-DTPA conjugates display enhance stability and beneficial paramagnetic properties. The adsorbtion of Gd-DTPA to CS-PAA nanoparticles should improve the efficiency of contrast agent delivery and minimize adhesion to blood components.
Results:
 |
|
Conclusion: CS-PAA nanoparticles can carry contrast agents like Gd-DTPA safely in neutral pH environments. At decreasing pH they gradually release their load. This pH sensitivity allows a targeted release at tumor sites. Furthermore, in vivo studies with anesthetized rabbits revealed an enhanced contrast of MRI images compared to single Gd-DTPA applications.
Source: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25846258
Intracellular sorting of differently charged chitosan derivatives and chitosan-based nanoparticles.
Zubareva A., Shcherbinina T., Varlamov V. and Svirshchevskaya E. Nanoscale. Vol.: 7 (17):7942-52. April 2015
The aim of this study was to examine differently charged chitosan derivatives with regard to their cellular binding, penetration and intracellular trafficking. The authors analyzed positively charged hexanoyl-chitosan (HC) and HC-based nanoparticles (HCNPs). Furthermore, succinoyl-chitosan (SC) and its nanoparticles (SCNPs) have been studied, which are negatively charged. The experiments were performed on epithelial (MiaPaCa and MDCK) and macrophage (RAW264.7) cell lines.
Results:
- binding to cell membrane: HC > SC > HCNPs and SCNPs
- epithelia cell penetration: SC and SCNPs > HC; HCNPs did not enter
- macrophages engulfed SC and SCNPs > HC and HCNPs
- pH dependent intracellular sorting
- SC and SCNPs transported to endosomes and lysosomes
- HC sorted to mitochondria
Conclusion: The binding, penetration and intracellular sorting of chitosan derivatives in human cells seem to be largely determined by the charge of the polymer. Positively charged derivatives were mainly sorted to mitochondria, while negative polymers co-localized with lysosomal compartments. These organelles possess different pH values (mitochondria: pH 8.0; lysosomes: pH 4.5) and might facilitate the neutralization of charged polymers. The findings of this study could help to improve efficiency and cellular specificity of chitosan-based drug delivery systems.